Postponing Repayment
Both Federal and private loan lenders provide students with in-school deferments and grace periods that delay when a loan enters repayment. Most loans are eligible for in-school deferment as long as a student is enrolled at least half time. Once a student drops below half time or graduates, deferments are usually followed by a six month grace period before payments are expected.
Grace Period
A loan’s grace period is a set period of time before a loan enters repayment, beginning when a student leaves school or drops below the set enrollment requirement. Except for federally subsidized loans, the interest on educational loans still accrues over grace periods.
Deferment
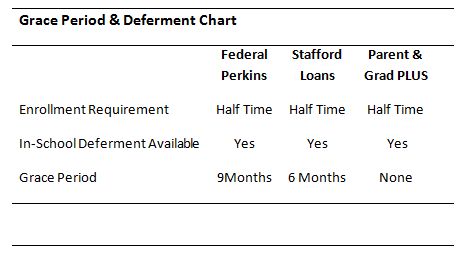 Deferments postpone loan repayment. However, interest still accrues during deferment except for subsidized loans. With federal loans, students are eligible for in-school deferment as long as enrolled at least half time. Once they have left school or graduated, repayment can be deferred if the borrower is unemployed or qualifies for an economic hardship deferment.
Deferments postpone loan repayment. However, interest still accrues during deferment except for subsidized loans. With federal loans, students are eligible for in-school deferment as long as enrolled at least half time. Once they have left school or graduated, repayment can be deferred if the borrower is unemployed or qualifies for an economic hardship deferment.
Forbearance
Forbearance allows loan payments to be temporarily paused, reduced or extended. The biggest difference between a deferment and forbearance is that interest will continue to accumulate for all types of loans, including subsidized. There are two types of forbearances available for borrowers who fail to qualify for loan deferment.
A discretionary forbearance is granted at the lender’s discretion based on illness or economic hardship. Mandatory forbearances require lenders to grant borrowers with extended time or reduced payments. These are usually awarded because of public service or economic hardship when monthly payments equal 20 percent or more of a borrower’s monthly income.
Bad Credit & Collection Companies
 Loans become delinquent with just one missed payment and remain in delinquency until all payments on the loan are brought up to date. Any loan in delinquency for 90 days or more is reported to major credit companies, causing the borrower’s credit score to drop significantly. After failing to make payments for 270 days or more on a monthly plan, loans enter default. Entering default is equated to breaking the legally binding promissory note and carries major consequences.
Loans become delinquent with just one missed payment and remain in delinquency until all payments on the loan are brought up to date. Any loan in delinquency for 90 days or more is reported to major credit companies, causing the borrower’s credit score to drop significantly. After failing to make payments for 270 days or more on a monthly plan, loans enter default. Entering default is equated to breaking the legally binding promissory note and carries major consequences.
Loan Consolidation
These loans combine more than one student loan into a single bigger loan from a single lender. Loans are often consolidated to reduce the size of a monthly payment by extending the current set loan term. A single and reduced monthly payment can help make repayment easier for borrowers.
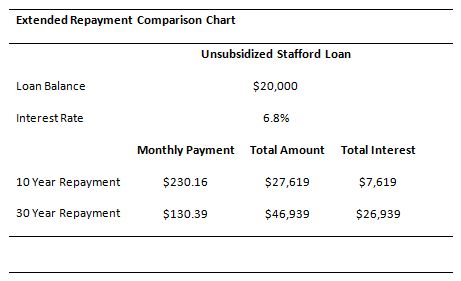 However, the total cost of the loan will increase from the additional interest added over the extended term. Borrowers with several loans may want to avoid consolidating. Keeping the loans separated allows the highest interest rate to be targeted and paid off faster.
However, the total cost of the loan will increase from the additional interest added over the extended term. Borrowers with several loans may want to avoid consolidating. Keeping the loans separated allows the highest interest rate to be targeted and paid off faster.
Consolidated loans must be from a single lender and so federal loans cannot be combined with private loans. Just as student borrowed loans cannot be consolidated with loans taken out by parents.
Federal Consolidation Loans
A federal direct consolidation loan is a fixed rate loan with an interest rate that is an average of the interest rates being consolidated. There is no additional cost or fees attached to consolidating federal student loans.
 Stafford Loans may only be consolidated once they have entered repayment. However, PLUS loans can be consolidated at any time. Perkins loans are also eligible for consolidation. However, borrowers will lose many of the loan’s benefits, such as subsidized interest, a nine month grace period and access to the loan’s generous forgiveness program.
Stafford Loans may only be consolidated once they have entered repayment. However, PLUS loans can be consolidated at any time. Perkins loans are also eligible for consolidation. However, borrowers will lose many of the loan’s benefits, such as subsidized interest, a nine month grace period and access to the loan’s generous forgiveness program.
Consolidating federal loans provides access to several different alternative repayment options that offer extended time from the standard 10 year repayment plan.
Private Consolidation Loans
If a borrower’s credit score has improved by 50 or more points since originally taking out the loans, consolidating private student loans could potentially provide a lower interest rate.
